Background
It is estimated that approximately 2% of the Indian population has a disability. Failing to provide equal access to technology for this demographic can result in limited access to essential government services and other vital infrastructure such as safety measures, logistics, healthcare, and education.
SugamyaWeb plays a crucial role in the pioneering Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan, launched by the Government of India in 2015. This visionary initiative aims to provide access to public infrastructure and services to people with disabilities, specifically focusing on improving web accessibility. Using automation and intelligent systems, SugamyaWeb drives testing and decision-making processes with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. It produces comprehensive audit reports enriched with practical guidance, recommendations, and visually appealing data analysis, enabling organizations to recognise and address accessibility challenges with advanced features such as root cause analysis and visualisation; SugamyaWeb is a catalyst for creating a more inclusive digital landscape in India. No organisation can afford to ignore the need for inclusive digital accessibility, and SugamyaWeb provides the necessary tools to ensure that all users can access and interact with web content.
What is Accessibility
Web accessibility, also known as eAccessibility, is about making websites on the Internet inclusive and accessible to everyone. It involves removing barriers that might prevent people with physical disabilities, situational disabilities, or limitations in bandwidth and speed from interacting with or accessing websites. The aim is to ensure that everyone can use the web without facing unnecessary obstacles or restrictions.
-
Cognitive
Ensuring that websites are designed in a way that accommodates individuals with cognitive disabilities, such as difficulties with memory, concentration, or problem-solving.
-
Visual
It's essential to make websites accessible for those with visual impairments. Include alternative text for images, clear fonts, and compatibility with screen readers.
-
Auditory
Websites should be accessible through captions, transcripts, and visual information to those with hearing impairments.
-
Motor
Make navigation easy for those with motor disabilities by ensuring keyboard accessibility and allowing alternative input methods.
-
Speech
Making websites accessible to those with speech impairments or disabilities requires providing alternate communication methods like text-based input or voice recognition.
The power of the Web is in its universality. Access by everyone regardless of disability is an essential aspectAs the web reshapes our world, we have a responsibility to make sure it is recognised as a human right and built for the public good.
“Tim Berners-Lee, W3C Director”
How do we make
website Accessible?
Sites are tested for compliance with GIGW (Guidelines for Indian Government Websites) which include guidelines, a subset of which are specific to accessibility. These guidelines are in conformance with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) which is a set of web standards that aim to make the Internet a more inclusive and accessible space for all.
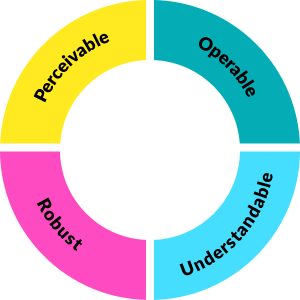
At a high level, WCAG sets out 4 key principles - Perceivable, Operable, Robust, Understandable. They provide a solid foundation to create web content that is accessible and usable for all.

How Was Sugamyweb Born?
To enhance the accessibility of the Indian Govt. webspace,the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) organised an Innovation Challenge in 2021-22. Many Indian startups participated in multiple stages of the challenge
Ideation
Numerous startups have presented their solutions to tackle the issue of evaluating the accessibility of Indian Government websites.
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
The shortlisted startups have formulated their iterations of a Minimum Viable Product, demonstrating their tool's proficiency in detecting accessibility issues.
Building a Functional Product
During the startup competition, the finalists showcased their impressive products that can identify accessibility issues and schedule tests at specific intervals. Their products also feature workflow capabilities that allow developers to track non-compliance fixes. Overall, their functional products significantly improve accessibility compliance.


